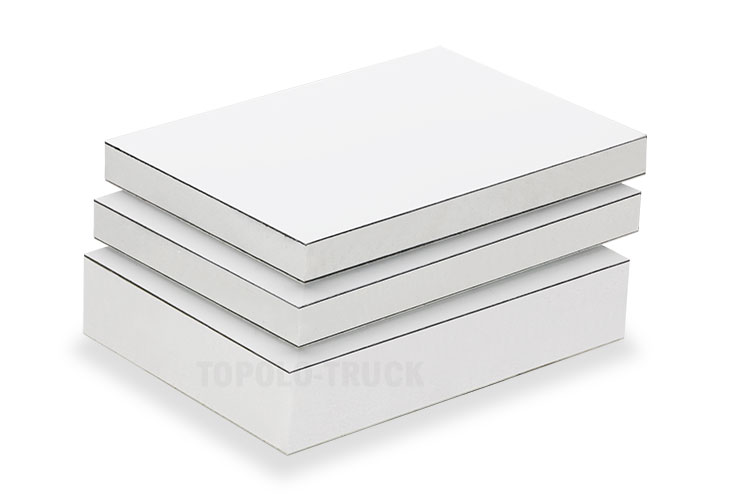

Fiberglass reinforced MPP foam sandwich panels are lightweight, high-strength, and recyclable composite materials designed specifically for box truck bodies. They are used in the structural design of refrigerated trucks, dry cargo trucks, RVs, and expedition vehicles.
Product Features
☑ Lightweight: Low density significantly reduces vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency and range.
☑ High Strength/Rigidity: The glass fiber layer provides excellent tensile and flexural properties, ensuring overall structural stability.
☑ Excellent Impact Resistance: The MPP foam core offers excellent cushioning and energy absorption.
☑ Waterproof and Corrosion-Resistant: The fully thermoplastic material system is non-absorbent and rust-resistant.
☑ Easy-Clean and Thermoformable: The surface can be selected from glossy, matte, or gelcoat finishes depending on the intended use.
☑ Recyclable and Environmentally Friendly: The all-thermoplastic construction meets vehicle lightweighting and sustainable development requirements.
Specifications of MPP Foam Sandwich Panels
| Width | ≤2.8m |
| Thickness | 10~150mm |
| Length | ≤12m |
| Core Density | MPP Foam. (Density:60~200kg/m³) |
| Skin | Fiberglass reinforced PP sheet. (thickness: 0.7-2.0mm) |
| Surface treatment | Glossy, matte |
| Processing | CNC Machining |
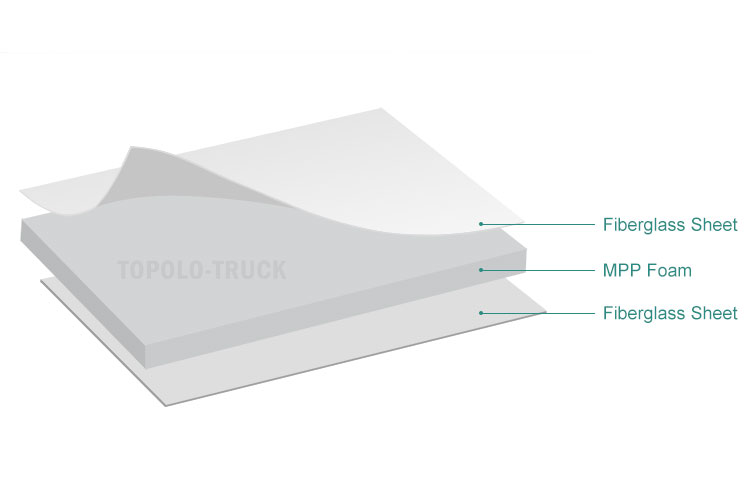
Structure
This composite panel combines a lightweight continuous fiber-reinforced polypropylene (PP) skin with closed-cell MPP foam. Both MPP and CFRT are thermoplastic materials, and the thermal lamination process allows them to bond tightly together, avoiding the delamination issues that can occur with traditional adhesive lamination.
What is MPP Foam?
Microcellular polypropylene foam (MPP) is a high-performance porous foam material characterized by its ultrafine pore structure. Its pore size is typically less than 100 microns (strictly defined as less than 10 microns), with a pore density exceeding 10⁹ cells per cubic centimeter. Compared to traditional foam materials, MPP foam offers a unique balance of mechanical properties: traditional structural foams are typically rigid and brittle, while soft foams are typically flexible and brittle. In contrast, microcellular polypropylene foam (MPP) combines both rigidity and toughness, achieving an ideal balance between lightweighting, energy absorption, and mechanical strength, thus filling the performance gap between existing foam materials.
Thanks to its excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and recyclability, MPP has become a core material for next-generation lightweight truck body structural composite panels.
